There are several entities involved in the successful transportation of a shipment.. However big or small a shipment is, two entities stand out due to the importance of their roles in a shipment..
These entities are a Freight Forwarder and a Clearing Agent..
It is very important to understand the functions of a freight forwarder and a clearing agent and their role in a shipment as this is often confused..
While in a lot of cases, a freight forwarder and clearing agent may be the same entity, there are many cases where they are different as well and in this post we explore the similarities and difference between a freight forwarder and clearing agent..
Who is a Freight Forwarder
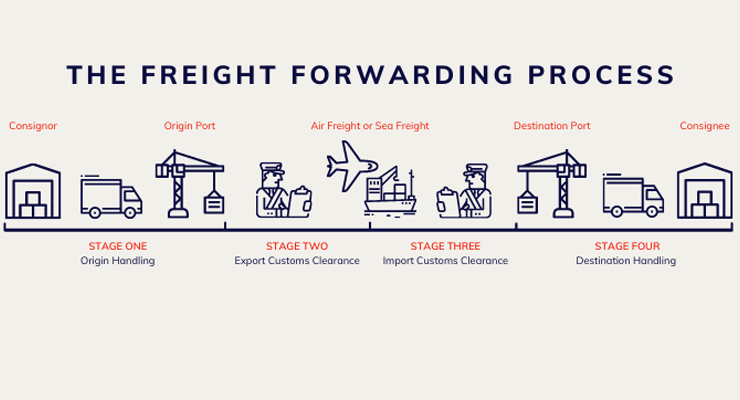
In the most succinct and layman terms, a Freight Forwarder is a multi-function agent/operator who undertakes to handle the movement of goods from point to point on behalf of the cargo owner..
The essence of freight forwarding is to ensure that the cargo is picked up from the seller and delivered to the buyer at the required place, at the right price and in the same condition that it is picked up from origin using the most suitable resources and routing possible..
If you are an importer or exporter imagine having to go through the activities of arranging trade and finance documentation, negotiating freight contracts, monitoring the movement of the cargo, transportation, customs clearances, port inspections and all other activities by yourselves for the above volume..
Especially if you don’t know about the intricacies of the industry or you a beginner to importing.. Daunting huh..!!
That is where a Freight Forwarder comes in.. A well established and experienced freight forwarder is expected to have below capabilities (either owned or outsourced)
experienced in all modes of transportation – road, rail, air and sea
able to provide cost-effective and efficient cargo shipping solutions based on the customer’s requirement
able to arrange storage for the cargo (usually all big forwarders have their own warehouses)
able to arrange the distribution or “forwarding” of the cargo as per the instructions of their client
have the capability to negotiate freight rates with the shipping line
able to book cargo with the shipping line as per the requirement of the client or under their own contract
process all relevant shipping documents such as certificates of origin, customs and port documentation, bills of lading and associated shipping/negotiating documentation (Eur1, Certificate of Origin, etc)
issue their own approved house bill of lading (HBL) although they are not an NVOCC
arrange transportation of the cargo from/to the customers’ premises and port
have a thorough knowledge of over border cargo movement
MAY or MAY NOT also do Customs Clearance
may or may not be accredited to customs, port etc and cannot do customs clearance if not accredited
acts as a carrier in cases where they issue house bill of lading
Who is a Clearing Agent
Every country has its own set of regulatory requirements relating to customs but one common requirement is that the clearing agent or customs broker (as they are referred to in a few countries) have to be accredited with the local customs authorities, border agencies, port and other authorities relevant to the shipment of goods..
They should have a valid clearing licence at the time of clearing the goods on behalf of the customer.. A few countries have very strict licencing requirements which are regularly reviewed and the agents that don’t follow these, may have their licences revoked..
A clearing agent is essentially an agent who specifically takes care of the customs clearance aspect of the business..
In many countries, clearing agents write examinations.. Only after the passing of this exam, they can transact as a clearing agent in that country..
USA and India are some of the examples where customs licence examinations are held..
Some countries like Australia however, seem to have stopped the customs examinations, preferring “acquired experience” over customs licence examinations for the purpose of licencing customs brokers..
Apart from the obvious function of lodging documentation with customs, a clearing agent has many other equally important responsibilities which affect them directly and also their clients..
A clearing agent
is a company accredited with the local customs authorities, border agencies, port etc
arranges to pass the relevant documents at customs
has in-depth knowledge of the HS Codes, the calculation of Duty and VAT
organises payment on the duty and VAT applicable
assists customers with duty drawback etc
does not negotiate freight rates with carriers on their own or on behalf of the client
does not issue own bills of lading in their capacity as a clearing agent
may be appointed by a freight forwarder or by the customer (exporter or importer)
When compared to a freight forwarder, a clearing agent is more specific to the country where they are based, as they deal directly and extensively with the local customs authorities and are au fait with the local requirements..
Freight Forwarders have more of a global presence since they may be present in a lot of countries compared to Clearing agents or Customs Brokers who tend to be more localised..
If you look at the above freight forwarders list, you may realise that all these freight forwarders have their own customs clearance department/divisions which means under normal circumstances and shipments, they would not use 3rd party customs clearing agents..
However, there might be cases where their role is only to handle the freight forwarding for the shipment whereas the customer appoints a different entity to handle customs clearance..
It all really depends on the contract of sales and the terms of shipment between the buyer and seller..
While a freight forwarder may be able to generate more revenue than a clearing agent, the big advantage that a clearing agent has over a freight forwarder is that their services will be required by the shipper and consignee FOR EVERY SHIPMENT, whereas the shipper or consignee might not use the services of a freight forwarder for every shipment..
So a customer necessarily needs the services of a clearing agent..
But, having said that, a lot of importers and exporters also have their customs clearing departments in-house which means they do not require the services of a 3rd party clearing agent..
One of the common goals/functions of these two entities is to advise their customers on the requirements to ensure a smooth shipment and arrange the same on behalf of the BCO.. So while two entities may have some overlapping activities, both are essential cogs in the wheels of global trade..







